Description
What is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal condition that affects about one in 10 women.
Ovulation occurs when a mature egg is released from an ovary. This happens so it can be fertilized by a male sperm. If the egg is not fertilized, it is sent out of the body during your period.
In some cases, a woman doesn’t make enough of the hormones needed to ovulate. When ovulation doesn’t happen, the ovaries can develop many small cysts. This cyst in ovaries produces an abnormal amount of androgens, male sex hormones that are usually present in women in small amounts. Women with PCOS often have high levels of androgens.
The 3 main features of PCOS are:
Irregular period: Which means your ovaries do not regularly release eggs (ovulation)
Excess androgen: High levels of “male” hormones in your body, which may cause physical signs such as excess facial or body hair
Polycystic ovaries: Ovaries become enlarged and contain many fluid-filled sacs (follicles) that surround the eggs.
What are the symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome?
If you have sign and symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, they’ll usually become apparent during your late teens or early 20s.
They can include:
• Irregular periods or no periods at all
• Difficulty getting pregnant as a result of irregular ovulation or no ovulation
• Excessive hair growth (Hirsutism) – usually on the face, chest, back or buttocks
• Weight gain
• Thinning hair and hair loss from the head
• Oily skin or acne
What are the complications with PCOS?
Complications of PCOS can include:
• Infertility
• Miscarriage or premature birth
• Type 2 diabetes or prediabetes
• Sleep apnea
• Depression, anxiety and eating disorders
• Cancer of the uterine lining (endometrial cancer)
• Metabolic syndrome — a cluster of conditions including high blood pressure, high blood sugar, and unhealthy cholesterol or triglyceride levels that significantly increase your risk of heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease
Obesity commonly occurs with PCOS and can worsen complications of the disorder.
What causes polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)?
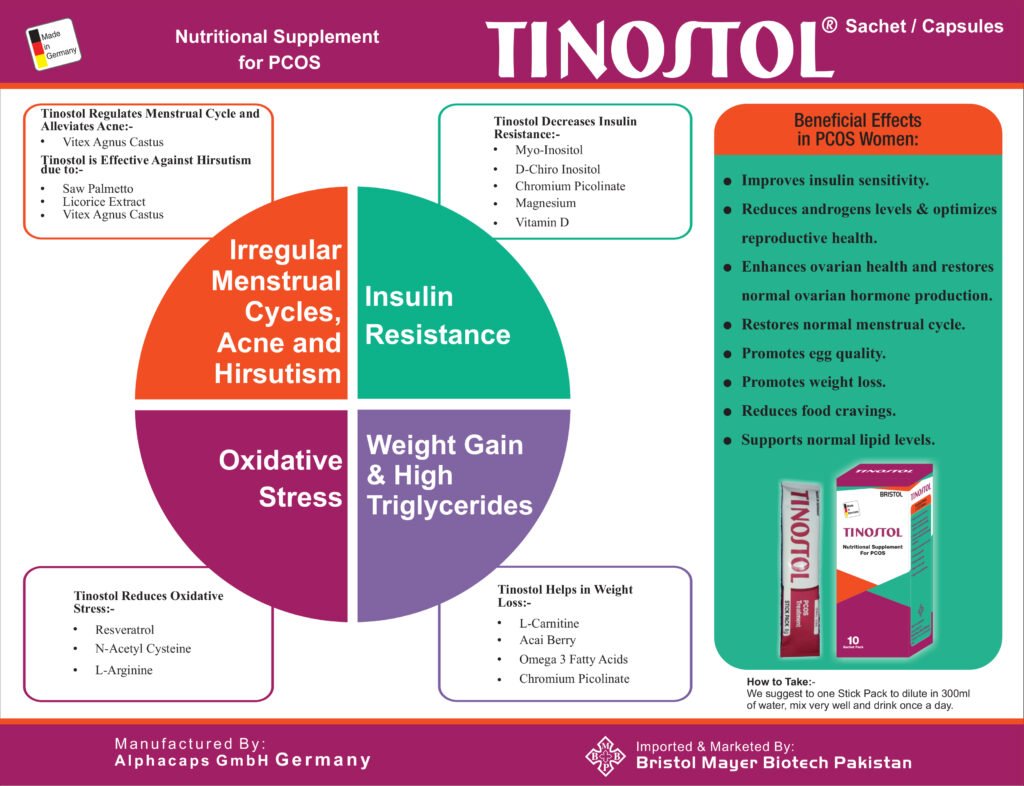
1. The exact cause of PCOS is unknown, but it often runs in families.
2. Being overweight or obese also increases the amount of insulin your body produces.
3. It’s related to abnormal hormone levels in the body, including high levels of insulin. Insulin is a hormone that controls sugar levels in the body.
Many women with PCOS are resistant to the action of insulin in their body and produce higher levels of insulin to overcome this. This contributes to the increased production and activity of hormones like testosterone.













62 reviews for TINOSTOL Capsules
There are no reviews yet.